
The Chipmunk uses a very rugged monoplane wing, which produces more lift and less drag than the biplane Tiger Moth.

The Chipmunk was carefully designed to overcome most of the problems of the Tiger Moth. Their pilots retained the traditional leather helmet.īy 1950 the Chipmunk had replaced the Tiger Moth. The RAF used the “chicken coop” canopy style you see on the Harvard and the Cornell.
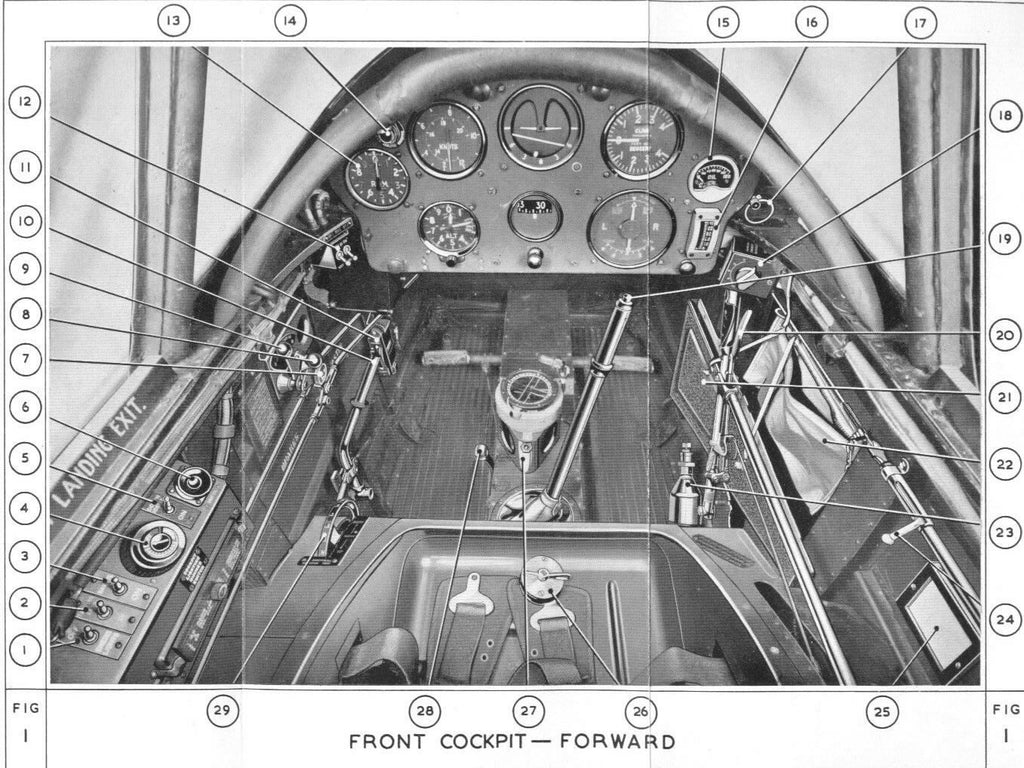
Canada wanted the bubble canopy that we see in the museum because there was room for the jet pilot-style helmet that would be used in later jet aircraft training.
#De havilland chipmunk license#
Soon Chipmunks were being built under license for the Royal Air Force. But the Royal Air Force discovered the Chipmunk and realized it was the ideal replacement for the Tiger Moth. The Chipmunk was designed and built in Canada. Their website contains a page that list all know Chipmunk aircraft with their construction numbers, registrations, histories and photographs where possible.Replaced the legendary Tiger Moth in October 1945.Ī total of 1,283 de Havilland Chipmunks were produced between 19. Today the Chipmunk remains a popular private aircraft, used for sport and aerobatics, as well as pilot training and tailwheel endorsements.Īccording to The de Havilland Aircraft Association of South Africa, a non-profit volunteer organisation based in Johannesburg, there were about 41 de Havilland Chipmunks that saw service in South Africa. In 1999, Gilles Leger developed a kit version of the aircraft to satisfy a growing homebuilding market around the world. Maximum speed - 138 mph (222 km/h) at sea level One 145-hp (108-kW) De Havilland Gipsy Major 8 inline piston engine Specifications: De Havilland Chipmunk T.Mk 10 The control stick also received a 76 mm extension for better control during extreme aerobatic manoeuvres. An example single-seat, sporting retractable landing gear, was flown in American colours for the 1970 world aerobatic championships. The Super Chipmunk, specially converted to become a better aerobatic aircraft, was fitted with a 260-hp (194-kW) Avco Lycoming GO-435 engine.


Another 60 aircraft were built under license in Portugal.ĭifferent variants of the Chipmunk were built to accommodate needs of different air forces around the world, including Canada, Portugal, Burma, Chile, Colombia, Denmark, Egypt and Iraq amongst others.Īfter WWII, the Chipmunk also became a popular civilian aircraft for training, aerobatics and crop spraying. In the United Kingdom, 1014 Chipmunks were built with the RAF receiving 735 of them for the Oxford University Air Squadron, and replacing the Tiger Moth at all 17 other university air squadrons. Manufacturing started in 1948 and 218 fully aerobatic Chipmunks were built in Canada between 19.
#De havilland chipmunk skin#
The all metal, low wing, tandem-seat stressed skin monoplane's prototype was powered by a 145-hp (108-kW) de Havilland Gipsy Major 1C and most Canadian versions were built with multi-panelled sliding canopies and later versions with a clear Perspex bubble canopy. Designed to succeed the iconic de Havilland Tiger Moth as a primary trainer for the Royal Air Force amongst others, the de Havilland Chipmunk flew for the first time on at Downsview, Toronto in Canada. The Chippie, as it is affectionately known, was designed by WJ Jakimiuk of de Havilland Canada in 1959.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
